What You Need to Know About Septic Systems
What Is a Septic System and How Does It Work?
In simple terms, a septic system is a holding tank in which natural bacterial action decomposes human waste products into environmentally acceptable components.
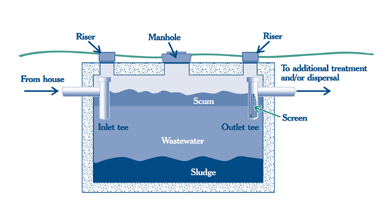 A septic system includes a septic tank, distribution box, and a septic field (also called an absorption field).In the septic tank, bacteria break down waste products into water, gas, and undigested material. This undigested material, sometimes referred to as sludge, is heavy and sinks to the bottom of the septic tank. Lighter material floats to the top of the septic tank.
A septic system includes a septic tank, distribution box, and a septic field (also called an absorption field).In the septic tank, bacteria break down waste products into water, gas, and undigested material. This undigested material, sometimes referred to as sludge, is heavy and sinks to the bottom of the septic tank. Lighter material floats to the top of the septic tank.
Inside the septic tank, baffles keep the heavy material at the bottom and the lighter material at the top from floating out of the septic tank. The septic tank has a vent system that allows gases produced in this process to be released into the air. Liquids from the tank flow into perforated pipes and then are metered out and absorbed into the septic field. The soil in the septic field also helps to filter out smaller solids present in the liquids. The heavy particles (sludge) at the bottom of the septic tank must be pumped out and disposed of every 2 years.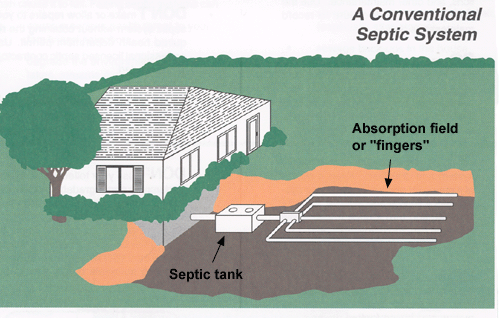
All Septic Systems Eventually Fail
Most septic systems will last about 25 to 30 years if they are properly maintained. However, all septic systems will eventually fail. The following factors contribute to and hasten the failure of septic systems:
-
Soil can clog the system: If sludge escapes into the distribution box and makes its way into the septic field, the soil in the field will become clogged with sludge, and liquids will no longer be absorbed into the soil. Not having the septic tank pumped regularly can lead to these kinds of clogs and can cause the septic system to fail.
-
Poor underlying soil conditions: If the soil in the absorption field is not capable of absorbing the liquids, the system can back up or puddles can develop at the grade level.
-
High water tables: During abnormally wet seasons, groundwater may rise into the septic field and force sewage upward to the ground surface. If this occurs, the system has to be re-installed at a higher level.
-
Roots can clog the system: Tree roots or plants can sometimes block the system. Removing the roots and clearing the pipes usually will remedy this.
-
Physical damage: Vehicles or heavy equipment passing over the system can cause damage to the underground pipes and connections.
Septic System Inspections
If the home you are purchasing has a septic system, we strongly advise that you consult with a professional for aseptic system inspection. Replacement of a failed septic system costs approximately $20,000 to $30,000. It is essential to find out whether the septic system is in good working order and has been properly maintained.
We recommend an open-pit septic inspection. This type of inspection involves removing the septic tank lid in order to inspect the septic tank baffles. During the inspection, the drain fields will also be probed using a long, heavy, metal rod to determine whether they are functioning properly.
We can arrange for a professional open-pit septic inspection to be performed at the time of your NJ home inspection. Alternatively, you can contract independently with any septic inspection company of your choice.
Want to Know More?
Information on Wastewater Management from the Association of NJ Environmental Commissions:
Environmental Protection Agency Septic System Resource
NJ DEP Homeowner's Manual for Septic Systems:
http://www.nj.gov/dep/dwq/pdf/septicmn.pdf
